History of N,N-DMT
N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is a powerful psychedelic compound found naturally in many plants and animals. It has been used for centuries in various traditional South American shamanic rituals, particularly as a key ingredient in ayahuasca, a psychoactive brew used for spiritual and healing purposes.
DMT was first synthesized in 1931 by Canadian chemist Richard Helmuth Fredrick Manske, but its psychoactive properties were not discovered until the 1950s. Hungarian chemist and psychiatrist Stephen Szára was the first to study its psychedelic effects in humans. During his experiments, he administered DMT to volunteers and documented the profound and intense experiences it induced.
In the 1960s, the counterculture movement brought increased attention to DMT and other psychedelics. However, its legal status soon changed, and it was classified as a Schedule I substance in the United States in 1970, making it illegal to manufacture, buy, possess, or distribute without a DEA license.
Despite its legal status, DMT remains a subject of scientific interest. Research has shown its potential for therapeutic applications, particularly in treating mental health conditions such as depression and PTSD. The unique and intense nature of the DMT experience continues to intrigue researchers and psychonauts alike.
Molecular Makeup of N,N-DMT
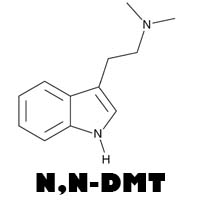
N,N-DMT, or N,N-Dimethyltryptamine, is a naturally occurring tryptamine with the chemical formula C12H16N2. Its molecular structure can be described as follows:
- Chemical Name: N,N-Dimethyltryptamine
- Molecular Weight: 188.27 g/mol
- Structure:
- DMT has an indole ring structure, similar to that found in serotonin.
- The molecule includes two methyl groups attached to the nitrogen atom of the tryptamine backbone.
Effects of N,N-DMT
N,N-DMT is known for its extremely potent and short-acting psychedelic effects. Common effects include:
- Visual and Auditory Hallucinations: Intense and vivid visual experiences, often described as entering otherworldly realms, accompanied by auditory distortions.
- Altered Perception of Time and Space: Time may seem to lose its meaning, and spatial awareness can become profoundly altered.
- Enhanced Sensory Perception: Increased sensitivity to sensory stimuli, with vivid and often surreal changes in perception.
- Emotional Intensity: Heightened emotions that can range from euphoria to fear.
- Spiritual Experiences: Deeply spiritual or mystical experiences, often involving encounters with non-human entities or otherworldly beings.
- Cognitive Effects: Changes in thought patterns, including profound insights and altered sense of self.
Typical Dosage
DMT is typically consumed by smoking or vaporizing, as it is not orally active without the presence of an MAOI (monoamine oxidase inhibitor). Dosages are measured in milligrams (mg):
- Threshold Dose: 2-5 mg (light effects, subtle changes in perception)
- Low Dose: 5-10 mg (mild to moderate psychedelic effects)
- Common Dose: 10-30 mg (full psychedelic effects, intense hallucinations)
- High Dose: 30-60 mg (strong and often overwhelming effects)
The onset of effects typically begins within seconds to minutes after inhalation, peaking at around 2-5 minutes, and can last 15-30 minutes. The intensity and rapid onset of the experience are characteristic of DMT.
Safety and Considerations
Due to its powerful effects, DMT should be used with caution. It is important to:
- Set and Setting: Ensure a safe, comfortable environment and a positive mental state.
- Dose Awareness: Start with a lower dose to gauge individual sensitivity.
- Presence of a Sober Guide: Having a trusted person who is not under the influence can help manage potential negative reactions.
- Legal Status: Be aware of the legal status of DMT in your country or region.
Research on DMT is ongoing, with studies exploring its potential therapeutic benefits, particularly in the treatment of mental health conditions such as PTSD, depression, and anxiety. However, due to its potent psychoactive nature, it remains a controlled substance in many areas.